Schneider Kft. project


Our company was asked by Schneider Ltd. to assist in increasment of production capacity and to produce a base drawing / utility survey drawing. The site is an industrial area of 7 hectares with 6 production halls, where the production of overhead travelling creanes with the largest manufacturing capacity in Hungary and the machining of steel structures is carried out.
In order to help in developing and growing the company, the managing director wants to build additional production halls and at the same time develop and modernise the site.
An existing map showing the landmarks was not available at the time, so we started with a production of a base drawing, showing in particularly high detail the surface and above-ground features, and we have surveyed the following objects:
Buildings, roads, pavement markings, parking lots, green areas, kerbs, ditches, gates, trees, levels, utility shafts, fire hydrants, overhead cables, poles, crane support poles, fire water storage pool, electrical distribution cabinets.
These points were measured using a Leica robotic total station and processed using N4ce software.
The final product is a 2D AutoCAD file that shows the entire industrial site in scale and with high geodetic accuracy.
The previously mentioned design base drawing was used as the basis for the utility survey which our company started surveying within 4-5 weeks after the survey for the base drawing has been completed.
During the utility survey, we aimed to locate and trace as many underground utilities as possible and measure their exact position. These included: electrical cables, water pipes, gas pipes, internet/optical cables, sewage, and utilities of unknown linear features (which we could not identify but our instruments indicated with high confidence). The utilities were plotted in 2D with textual depth data.
Two main instruments normally used for any the utility survey. An electro- magnetic locator (EML), which can locate cables/pipes that contain metal. The other instrument we used was a ground penetrating radar (GPR). This instrument is a kind of confirmation of the utilities detected by the EML and it can also detect plastic pipes with high accuracy without digging up
the ground.
GPR can also be used to make assumptions on the structure/composition of the soil, which can be of great help during construction, e.g. what soil not to build a building on.
Advantages of a site survey:
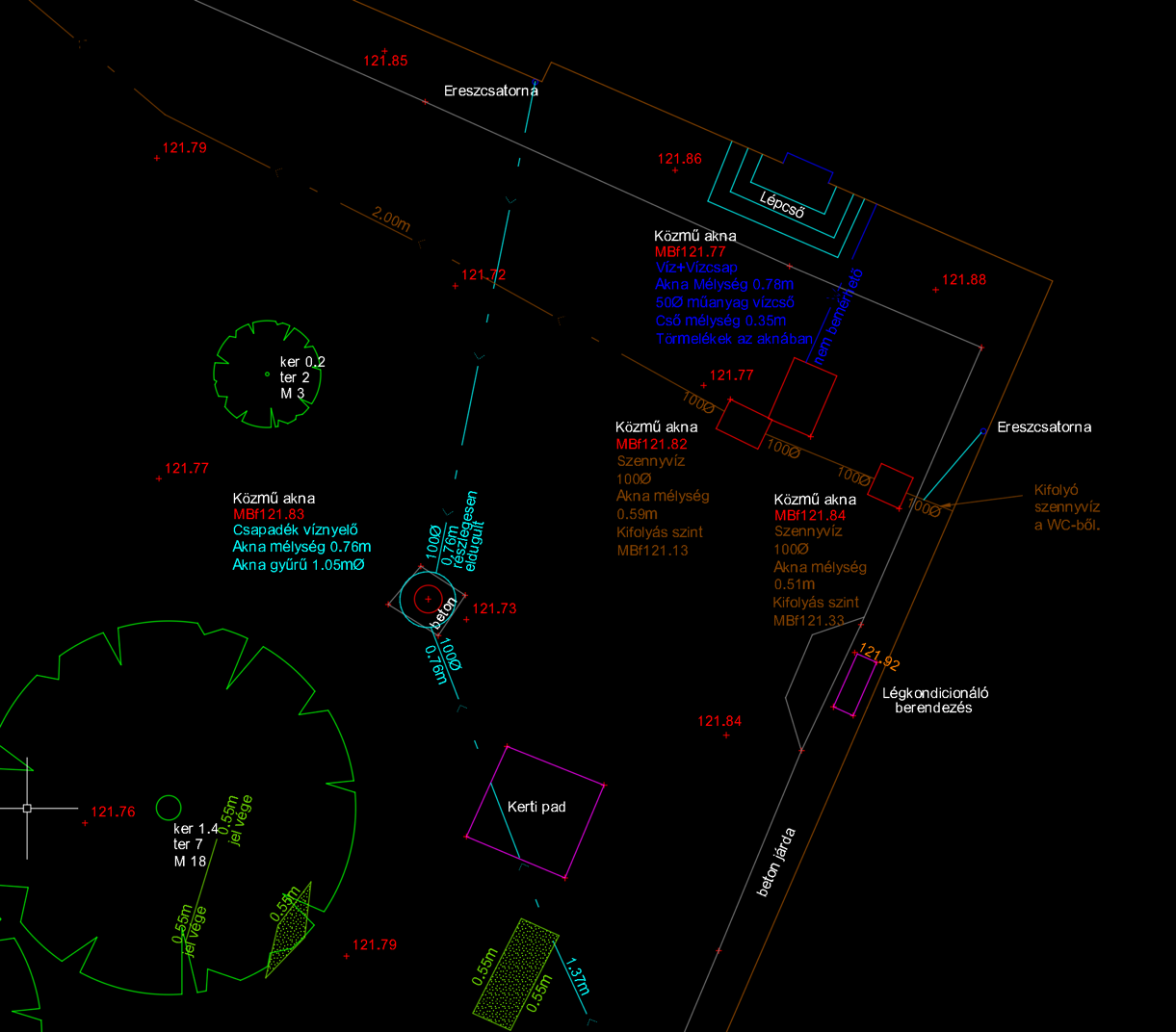
a, the utility survey facilitates site maintenance and assists branch planning

b, provide a comprehensive view of the current state of the site and support decision making
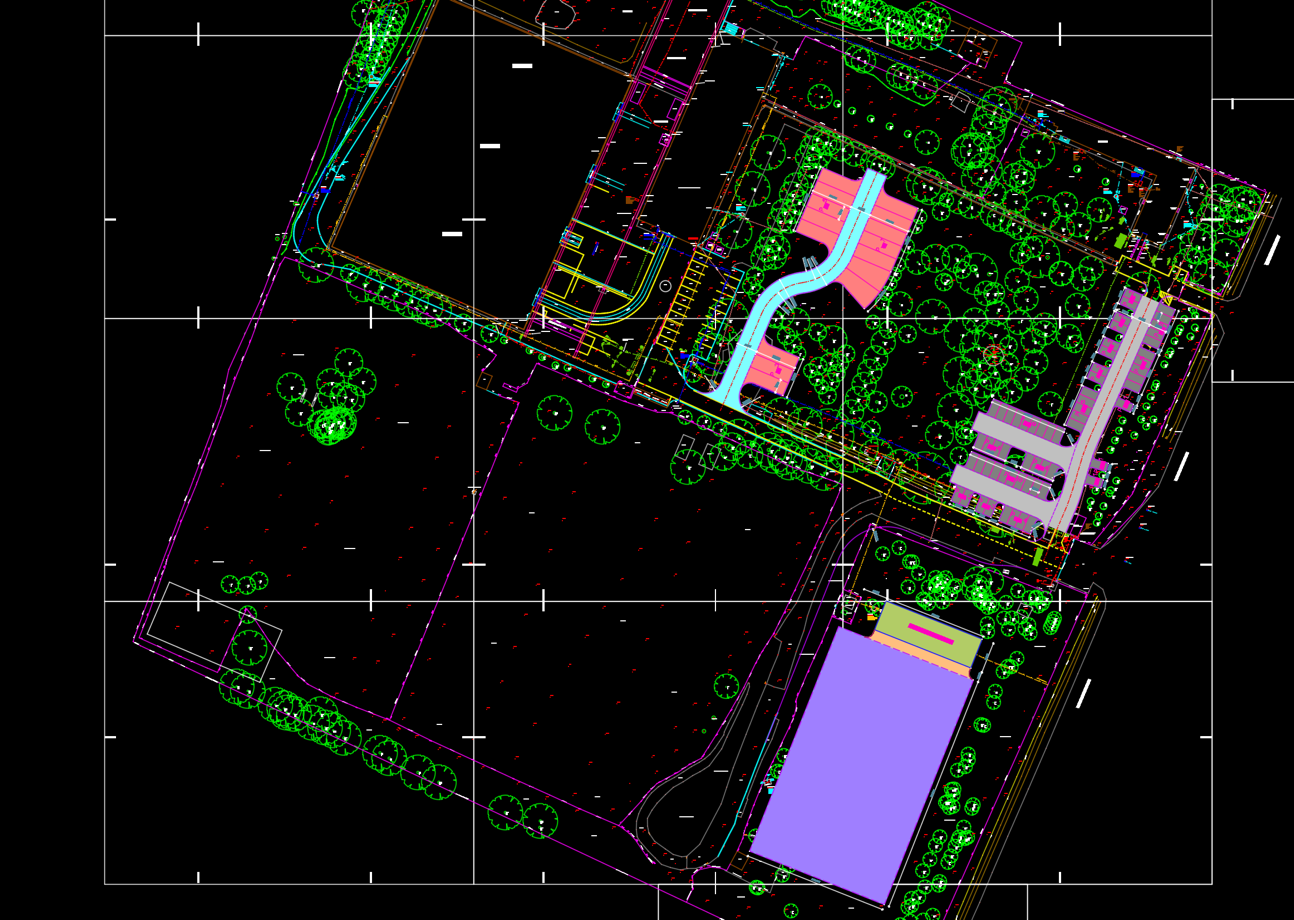
c, a complete site survey facilitates planning for improvements